Europe and Central Asia Enter 2026 with a Slowing Economy
In the first half of the year, there was moderate trade growth, largely driven by anticipatory purchases of goods ahead of expected tariff increases. Although global financing conditions have improved, with a decrease in sovereign spreads and strengthening stock markets, external risks remain. Weak economic dynamics in the Eurozone and uncertainty in trade policy negatively affect exports, especially in the automotive sector of Central Europe and the Western Balkans.
After a slowdown at the beginning of 2025, inflation in the region began to rise again in the second half of the year.
Prices are under pressure from rising food and utility costs, particularly in Central Asia and Romania, as well as from ongoing wage growth. Most central banks preferred to keep the current monetary policy unchanged.
According to the World Bank's forecasts, economic growth in ECA will remain at 2.4% in 2026. Domestic demand is expected to be supported by declining inflation, improved financial conditions, the absorption of EU funds, and increased defense spending. A moderate recovery in exports is anticipated in 2027.
The growth rates for the countries in the region, excluding Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine, are expected to be approximately 3.1% in 2026-2027. However, there are significant demographic challenges among the forecasts, such as an aging population and a declining labor force growth. By 2050, the dependency ratio could reach 63%.
The risks associated with the forecast remain high. Increased trade tensions, prolonged geopolitical conflicts, and a potential rise in global interest rates could negatively impact economic indicators. At the same time, if the active phase of the conflict in Ukraine ends sooner, it could facilitate an acceleration of investments in recovery and increase investor confidence.
In the global context, economic stability is maintained: global economic growth is expected to be 2.6% in 2026 and 2.7% in 2027. However, a quarter of developing countries are still poorer than they were in 2019.
Read also:
What the Labor Market in Kyrgyzstan Was Like in 2025: Salaries, Job Vacancies, Regional Rankings
The labor market is a reflection of social and economic processes, and analysts from the platform...
"Ay-Pery" has transformed into an international business center — photo report
Curl error: Operation timed out after 120001 milliseconds with 0 bytes received...

Aeon: How the Conquest of Foreign Territories Came to Be Considered Unacceptable
Author: Cary Goettlich In the modern world, there are fewer and fewer things that evoke consensus...
The Economy of Kyrgyzstan - 2025: Growth Records and Price Shocks
In 2025, Kyrgyzstan found itself at a crossroads, facing stark contrasts in its economy. On one...

The National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic presented new rules for financial marketplaces
The National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic (NB KR) has presented a draft of new rules regarding the...

Bishkek Enters the Cycle of Revaluation of the Royal Central Park Real Estate Market and the Advantage of Price Fixation in the First Three Years
The economy, which is on the path of rapid and stable growth, leads to an increase in real estate...
A Year of Turbulence and Pragmatism. What 2025 Will Be Remembered For and What to Expect in 2026
The outgoing year 2025 was marked by significant global turbulence and a new perspective on...
Tokayev: Kazakhstan has entered a new stage of modernization
Curl error: Operation timed out after 120001 milliseconds with 0 bytes received...
Forecast for 2026. How prices will rise and what will become the most expensive
In 2025, residents of Kyrgyzstan faced financial difficulties due to rising prices outpacing their...
Torture of Patients. The GKNB Reveals Shocking Rehabilitation Methods at the "Path to Life" Center
Curl error: Operation timed out after 120001 milliseconds with 0 bytes received...
The global economy will grow by 2.7 percent in 2026 - UN report
According to a report by the United Nations, the global economic output is expected to grow by 2.7%...
In 2025, inflation in Kyrgyzstan was influenced by external factors, - National Bank
In 2025, Kyrgyzstan faced inflationary pressure caused by external factors. This was reported at a...
Forecast for 2026. What Awaits the Economy of Kyrgyzstan and What Risks Does It Face
The economic year is coming to an end, and for Kyrgyzstan, it has turned out to be quite...

Why the U.S. Should Include the Turkic States Organization in Its Policy Toward Central Asia - The National Interest
The visit of Kubanychbek Omuraliev, the Secretary General of the Organization of Turkic States, to...

Kyrgyzstan Among the Leaders in Economic Growth in Central Asia in 2026
According to forecasts, Kyrgyzstan, along with Tajikistan and Uzbekistan, will be among the...
NBKR: The current account deficit will remain at 23.2% of GDP in 2025, and 21.3% in 2026.
- In its latest report on monetary policy, the NBKR presented a forecast for the balance of...

Kubat Umurzakov: China Becomes the Main Trading Partner of Central Asia for the First Time in History
Central Asia, where the "One Belt, One Road" program was initiated for the first time,...

Chinese Industry Loses Profit Amid Economic Slowdown
In November, the profits of Chinese industrial companies fell at a record pace, marking the...
The Ombudsman checked the conditions of detention in women's colony No. 2
Curl error: Operation timed out after 120001 milliseconds with 0 bytes received...
"Sometimes Harsh, but Necessary". How Entrepreneurs Assess the Year 2025
According to the analytical forecast of the Central Bank, it is expected that by the end of 2025,...

Ambassador of China to Kyrgyzstan: China's trade turnover with Central Asian countries has exceeded $100 billion for the first time
Central Asia is the region where the "Belt and Road Initiative" was first proposed, and...

Turkey expands its influence in Central Asia and challenges Moscow
According to BZ, Turkey is actively expanding its influence in Central Asia by implementing...

The National Bank of Kyrgyzstan has maintained the discount rate at 11%
During the meeting on January 26, 2026, a decision was made to maintain the discount rate (key...
NBKR: Inflation is expected to be at 10.5–11% by the end of 2025
- According to the materials from the National Bank of the Kyrgyz Republic, inflation in the...
How "Eurasia" is Changing the Daily Lives of Millions in Kyrgyzstan
Curl error: Operation timed out after 120001 milliseconds with 0 bytes received...
The Economy of Kyrgyzstan Will Maintain Leadership in the Region for GDP Growth - EDB Forecast
According to forecasts, in the coming year, Kyrgyzstan's economy will take leading positions...
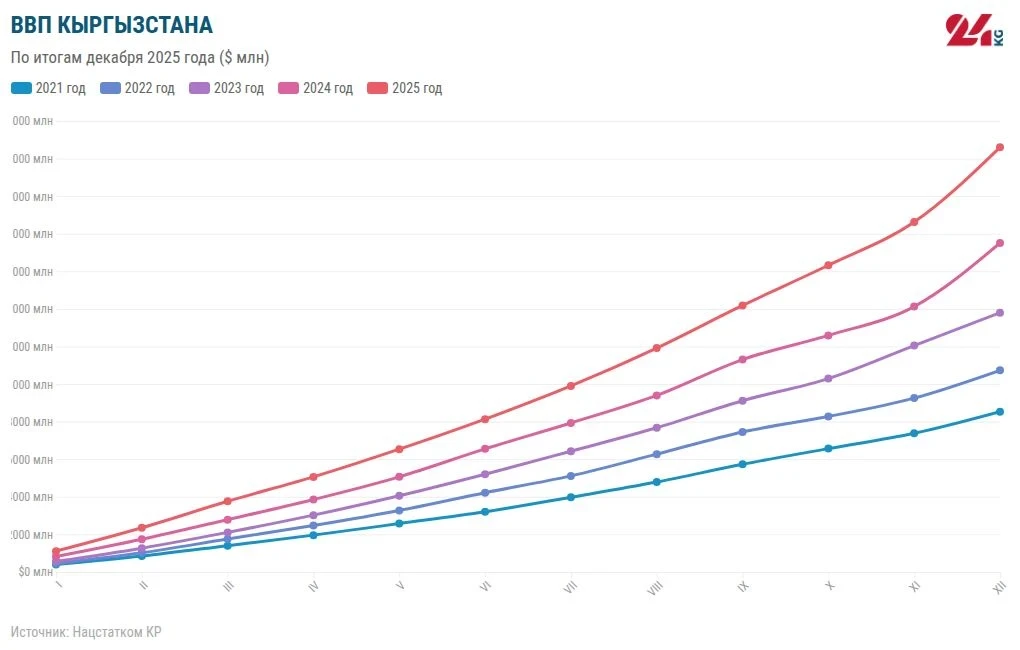
The Economy of Kyrgyzstan Grew by 11.1 Percent: Results of 2025
According to preliminary data, the gross domestic product (GDP) of Kyrgyzstan in 2025 amounted to...
UN forecasts a decrease in inflation to 3.1% and moderate global economic growth at 2.7% in 2026
- During the briefing, Shantanu Mukerji, the Director of the UN Department of Economic Analysis and...

To Avoid Inflation and Preserve Value: What Should Investors in Bishkek Do?
In the context of global economic instability and the resurgence of inflation, the period from...
Stable, Pragmatic, and Gradually Developing Relations - Ambassador of Kazakhstan Rapil Zhoshybaev (Interview)
The Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary Ambassador of Kazakhstan to Kyrgyzstan, Rapil Zhoshybaev,...

The State Committee for National Security of the Kyrgyz Republic donated 1 million soms and gifts to the special school for the hearing impaired.
On December 26, 2025, the Chairman of the State Committee for National Security of the Kyrgyz...

The GKNB donated 1 million soms and gifts to the special school for the hearing impaired.
On December 26, 2025, the chairman of the GKNB, Kamchybek Tashiev, visited a specialized school...
UN Report: Central Asian Countries to Maintain Steady Economic Growth in 2026
According to a new UN report, growth in 2025 was 2.2%, and a decline to 2.1% is expected in the...

A Major Loan Shark and Owner of a Pawnshop Chain Arrested
In Bishkek, law enforcement agencies detained a well-known loan shark and owner of a chain of...

A Unified Policy for Livestock Markets Will Be Implemented in the Chui Region
A unified policy regarding livestock markets will be implemented in the Chuy region. This was...
The NBKR updated its medium-term forecast: GDP growth is expected to be around 9.5% in 2025, and up to 9% in 2026.
- In its monetary policy report for the third quarter of 2025, the National Bank of the Kyrgyz...
Growth of developed economies will be 1.8% in 2026 compared to 1.7% in 2025, - IMF
- The GDP growth forecast for developed economies is 1.8% in 2026, according to the January IMF...

Russian and Ukrainian Drone Manufacturers Buy Components from the Same Chinese Companies
According to The Financial Times, Russian and Ukrainian drone manufacturers are using the same...

The National Bank of Kyrgyzstan has maintained the key rate at 11%
On January 26, 2026, the Board of the National Bank of Kyrgyzstan decided to maintain the interest...
10 Key Events in the Relations Between Central Asian Countries and China in 2025
Strengthening Friendship and Expanding Cooperation in Central Asia In 2025, there is active...

Zelensky spoke about the 20 points of the peace plan. What's new in it?
President of Ukraine Volodymyr Zelensky presented a draft agreement for ending the war, which was...

"Europe is Being Taken 'by Surprise': How Trump's Policies Affected the Old World"
Photo DER SPIEGEL The crisis related to the potential annexation of Greenland has revealed the...

Tokaev gave a major interview to the Turkistan newspaper. It covers reforms, AI, nuclear power plants, Nazarbayev, and much more.
President Kassym-Jomart Tokaev shared his views on current challenges and achievements in his...
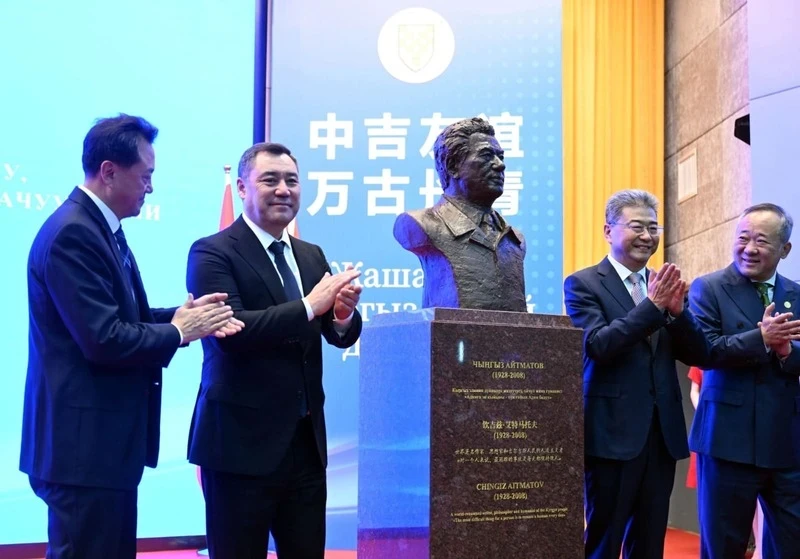

Visited more than 10 countries. Where did Sadyr Japarov travel this year?
In the outgoing year of 2025, the President of Kyrgyzstan, Sadyr Japarov, made 23 trips abroad,...
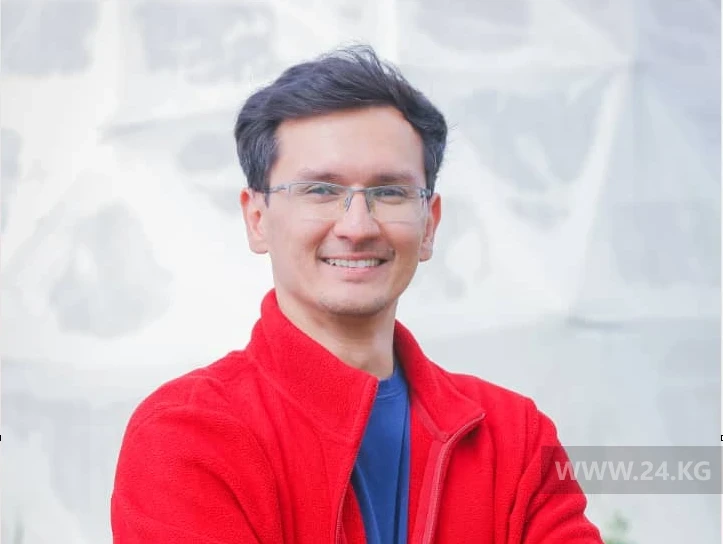

Economic Results of 2025: Seven Landmark Events in the Economy of Kyrgyzstan
Economist Arsen Imankulov provided an analysis of the economic results of 2025 for 24.kg,...
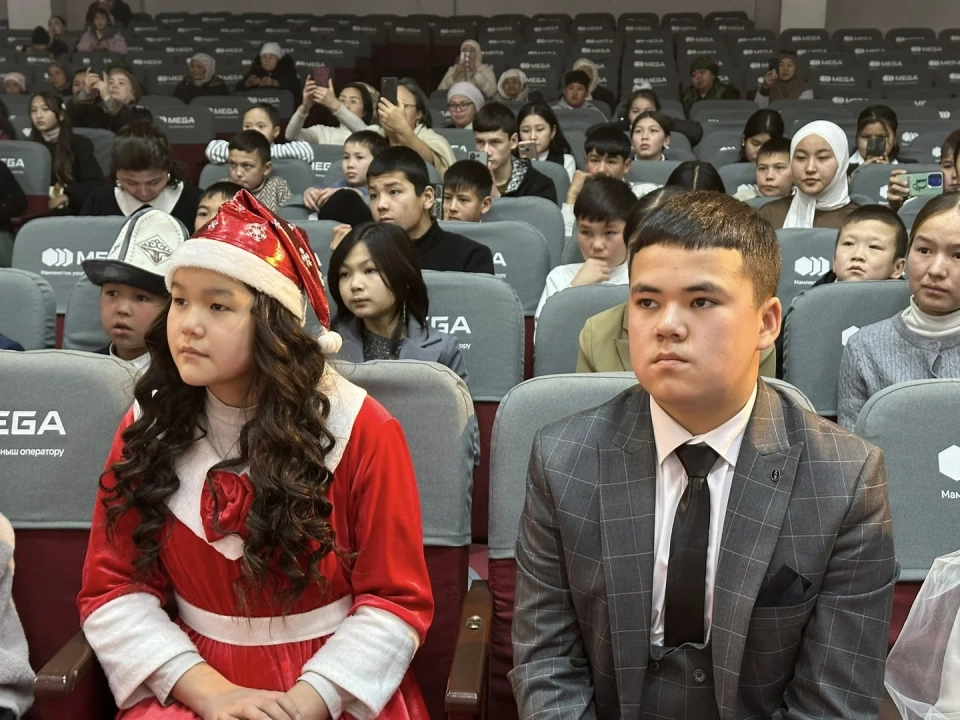

In Batken, children were shown a New Year's fairy tale and received gifts from the regional leadership.
In Batken, a New Year's celebration for children was held, organized by the presidential...
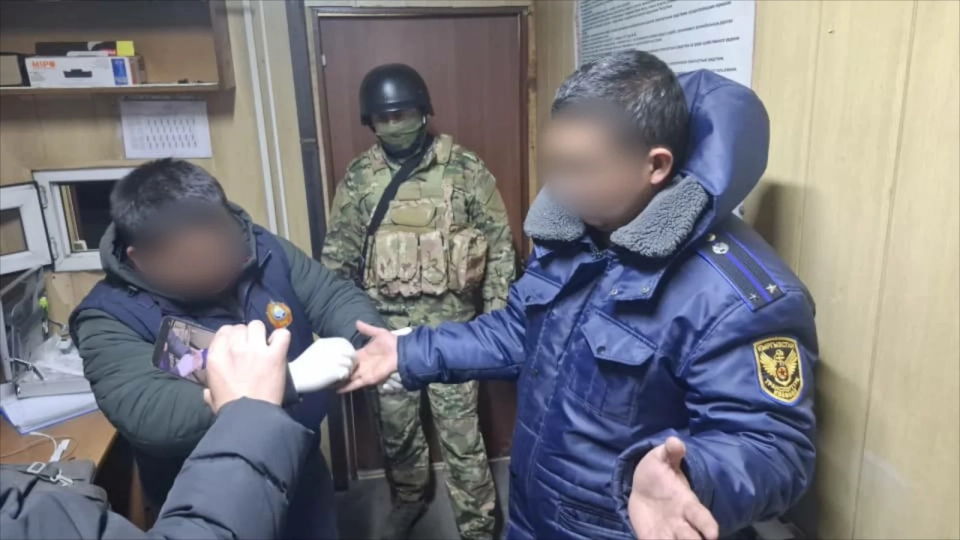

Employees of weight and dimension control detained for extorting money from drivers
As a result of operational measures, seven employees of the weight and dimension control on the...