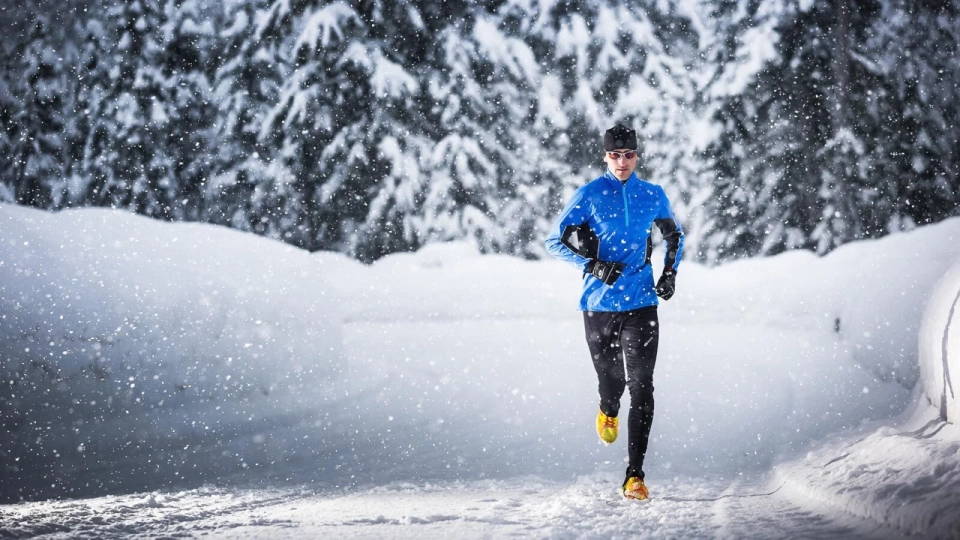
The conclusions are based on data collected over many years of observation, during which scientists studied the real impact of exercise variety on mortality rates. Participants in the experiment engaged in various sports, including running, cycling, swimming, rowing, gymnastics, tennis, squash, strength and aerobic training, yoga, stretching, and gardening.
The results showed that those who exhibited the greatest variety in physical activity had a 19% lower risk of premature death. The researchers accounted for numerous lifestyle and health factors of the participants.
Notably, the variety of physical activities had a positive impact on life expectancy regardless of the total time spent training. The authors of the study emphasize that engaging in different sports can provide additional health benefits, which is especially relevant for people with chronic diseases who need physical activity.
It is also worth noting that the results of this study resonate with the findings of another group of scientists who previously established that physical exercise slows down the processes of epigenetic aging.