Natural disasters were recorded everywhere, causing serious damage to the environment.Celeste Saulo, head of the WMO, noted that the nature of extreme weather conditions makes them one of the main risks mentioned in the annual report of the World Economic Forum on global threats. The number of people suffering from climate disasters is increasing, and January became a vivid example of their tragic consequences.
She also added that in countries with effective early warning systems, the mortality rate from natural disasters is six times lower, highlighting the relevance of the "Early Warning Systems for All" program.
Winter Storms and Frosts
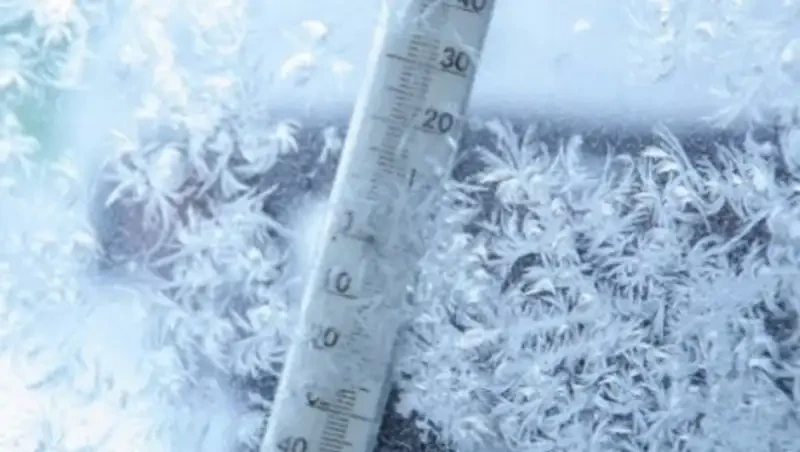
Despite the fact that, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the frequency of severe cold worldwide has been decreasing since 1950, powerful cold snaps still occur. The weakening of the polar vortex has led to an intrusion of Arctic air into temperate latitudes, causing sharp frosts in North America, Europe, and Asia. These cold conditions are associated with a large area of cold air and strong winds that usually circulate around the Arctic.In Kamchatka, over two meters of snow fell in the first two weeks of the month, with an additional 3.7 meters in December, marking one of the snowiest periods since the 1970s. In Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, traffic was almost paralyzed, and snowdrifts hindered access to important buildings.
At the end of January, a powerful winter storm hit Canada and the USA, leading to widespread power outages, flight cancellations, and human casualties. The National Weather Service of the USA warned that by January 31, a new wave of Arctic cold would envelop the south, including the plains states and the Great Lakes.
Some meteorological forecasts also predict that stratospheric warming over the Arctic may lead to a significant weakening of the polar vortex in early February, creating conditions for a new intrusion of cold air into North America and Northern Europe in the second half of the month.
Floods and Heavy Rains
Europe faced a series of storms accompanied by heavy precipitation and flooding, affecting Ireland, the UK, and Mediterranean countries. Meteorologists warned of continued elevated precipitation in Northwestern Europe and the Mediterranean.The situation in Southern Africa proved particularly challenging. According to Mozambican authorities, floods affected over 650,000 people, with hundreds of thousands forced to leave their homes, and about 30,000 residences damaged or destroyed. South Africa declared a national disaster due to heavy rains that claimed the lives of dozens of people.
Hot Conditions and Fires
Australia experienced two heatwaves in just one month. In Ceduna, temperatures reached a record 49.5 degrees Celsius. Scientists note that climate change has made January's heat 1.6 degrees more intense.In Chile, wildfires claimed the lives of at least 21 people, and tens of thousands were evacuated. Fires also spread across southern Argentina. According to the IPCC, human-induced climate change has increased the frequency and intensity of heatwaves since the mid-20th century.
The Importance of Early Warning Systems
The World Meteorological Organization is actively working to reduce the impacts of extreme heat and other weather threats, including through collaboration with the World Health Organization.January 2026 served as yet another important reminder that investments in early warning systems, climate resilience, and disaster preparedness can save many lives.
Photo on the main page is illustrative: idea.int.