The doctor named the key risk factors for the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child
The article emphasizes that vertical transmission of the hepatitis B virus is a serious problem in perinatal medicine, as it can lead to chronic HBV infection in newborns.
The study was based on the analysis of medical data from 231 pregnant women with chronic HBV infection. The work evaluated both serological and molecular-biological parameters, as well as laboratory indicators, including APRI, which demonstrates the level of liver fibrosis.
The results showed that an increased APRI index in pregnant women is a key factor that raises the risk of giving birth to HBsAg-positive children. This highlights the need to assess the state of liver fibrosis to predict the likelihood of virus transmission.
The study also confirmed the high effectiveness of combined prevention: vaccination of newborns along with the administration of specific immunoglobulin (HBIG) provided complete protection against the virus. In contrast, when only the vaccine was used, the hepatitis B virus was detected in 13.1% of children.
The article states that vertical transmission of the virus can occur at all stages of chronic HBV infection, even with low viral load. Early use of antiviral therapy with tenofovir in combination with vaccination demonstrated high effectiveness and can be considered as an alternative to regimens with HBIG.
The author of the study concluded that the best strategy for reducing the risk of hepatitis B transmission from mother to child is a combination of antiviral treatment for the mother and specific immunoprophylaxis for the newborn.
Read also:

250,000 Doses of Hepatitis Vaccines Arrive in Kyrgyzstan
The vaccines will be available free of charge...
250,000 Doses of Hepatitis Vaccines Arrive in Kyrgyzstan
A batch of 250,000 doses of hepatitis vaccine has arrived in Kyrgyzstan, as reported by Deputy...
The Ministry of Health received 250,000 doses of hepatitis vaccines.
At the meeting of the Jogorku Kenesh Committee on Agricultural Policy, Water Resources, Subsoil...
Medical Myths. For over 30 years, statins have saved lives, but why do people still dislike and fear them?
The opinion of Professor Igor Pershukov on statins and the debunking of misconceptions. I.V....
Residents of the cities of Tash-Kumyr and Shamal-Say complain about the rise of hepatitis among the population, - deputy
At the meeting of the Jogorku Kenesh on January 14, Deputy Kunduzbek Sulaymanov expressed concern...
In Kyrgyzstan, the incidence of whooping cough among older children has increased, - study
In Kyrgyzstan, there is a growing incidence of whooping cough, which previously primarily affected...
The flu season has become longer, and the number of cases has increased over the past three years.
This year, the flu started earlier and is spreading more intensively. This is associated with the...
In Kyrgyzstan, adolescents who use nicotine are more frequently found to have high blood pressure, - study
In Kyrgyzstan, a study was conducted to examine the prevalence of tobacco smoking and vaping among...

On the Eve of the New Year, a Doctor Reminded About the Dangers of Mixing Alcohol and Medications
With the arrival of the New Year, therapist Nargilya Chomokeeva from the Family Medicine Center...

In Tash-Kumyr, the number of cases of hepatitis and liver cirrhosis is on the rise
The deputy requested clarifications from the authorities...
Weight loss in middle age may have negative consequences for the brain
Specialists from Ben-Gurion University, located in the Negev, Israel, conducted a study that...

When replacing driver's licenses, free testing for hepatitis and HIV is offered
The procedures for testing and vaccination are voluntary In Kyrgyzstan, changes have been made to...

WHO warns of the spread of a new flu variant: vaccination remains the best protection
Wenqin Zhang reported that influenza and other respiratory viruses are actively spreading this...

Fatty cheeses and creams are associated with a lower risk of dementia
According to a conducted study, participants who consumed at least two slices of fatty cheese...
During the issuance of certificate 083, medical professionals suggest undergoing tests for hepatitis and HIV.
Citizens of Kyrgyzstan who are changing their driver's licenses can take the opportunity to...
How Magnesium, Zinc, and Copper Affect Sleep Quality: Research Results
According to a study conducted on more than a thousand adults, sleep quality may be related to...
In the third quarter of 2025, over 800 children found families in Kyrgyzstan
The Ministry of Labor, Social Protection, and Migration of the Kyrgyz Republic has published the...
AI has learned to predict the unemployment rate in the USA based on social media.
A team of researchers from New York University, Oxford, the World Bank, and Ben-Gurion University...
Scientists link the consumption of dark chocolate to the slowing of biological aging
Specialists from the Royal College of London published their findings in the journal Aging, where...
In Kyrgyzstan, the Most Effective Method of Surgical Treatment for Prostate Adenoma Has Been Identified
Benign prostatic hyperplasia remains one of the most common urological diseases among men over 60...
Conversation while driving slows down eye reactions, increasing the risk of accidents
Recent research conducted by scientists from Fujita Health University has revealed that...

The Ombudsman of the Kyrgyz Republic appealed to government agencies due to the murder of a mother of three children.
This appeal was prompted by the tragic death of a 47-year-old woman, a mother of three children....

An Unexpected Link Between COVID-19 and Alzheimer's Disease Revealed
In a new study conducted by scientists from Stony Brook University and published in the journal...

Ministry of Labor of Kyrgyzstan: In the third quarter, more than 800 children found families
In the third quarter of 2025, the Ministry of Labor, Social Protection, and Migration published...

Physical Exercise Leads to Cancer Suppression: Study by Australian Scientists
Bias related to knowledge of the outcome is equally prevalent in both sports and the office....

Municipal Inspection and District Akimats Received Official Vehicles
In anticipation of the holiday, the mayor of the city, Aibek Junushaliev, handed over official...
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is spreading in Kyrgyzstan — it occurs in every third person, according to a gastroenterologist
According to Mamiraim Jumabaev, head of the gastroenterology department at the National Center for...
Expansion of financial instruments and the opening of the border with Tajikistan supported small businesses, - MDS
Factors contributing to business development in Kyrgyzstan, including the expansion of financial...

The world no longer has the classic four seasons, scientists say
The key findings of the study challenge the existence of a universal model of four seasons. The...
In which region of Kyrgyzstan is cancer most frequently detected and which type is the most prevalent? Research data
By the beginning of 2025, the National Center for Oncology and Hematology of the Ministry of Health...
Two Hours of Help a Week Slows Brain Aging by 20%
Research conducted by scientists from the University of Texas and the University of Massachusetts...

Young ants can plead with their "brothers" for death: what is the reason?
In contrast to pupae, worker ants can leave the nest in case of illness, while pupae do not have...
Standing on one leg helps strengthen muscles, improve memory, and maintain brain health, - rehabilitation medicine specialist
As we age, balancing on one leg becomes more challenging; however, as Tracy Espiritu McKay, a...

"Such a crime cannot be justified": Kamchybek Tashiev made a harsh statement regarding the murder of a Bishkek resident
The head of the State Committee for National Security expressed his feelings about the terrible...
Children of the woman shot in Bishkek will receive psychological support
After the tragic death of 47-year-old U.J., a mother of three, the Ombudsman of Kyrgyzstan, Jamila...
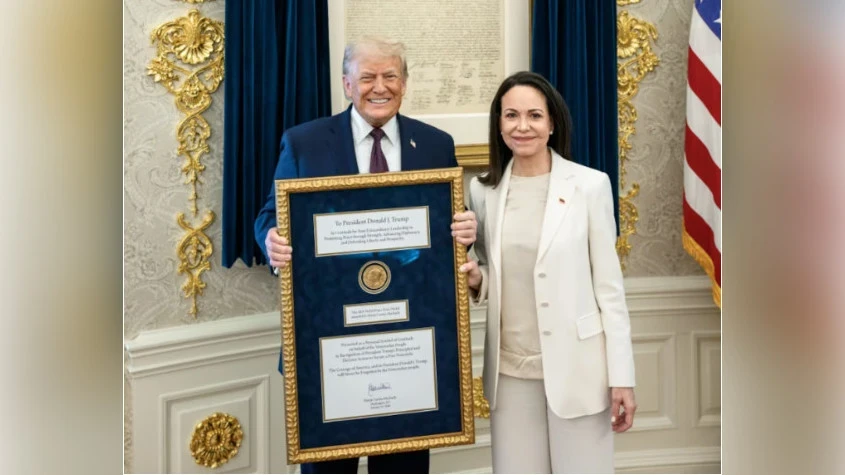

The Nobel Committee commented on the awarding of the Peace Prize to Trump
The Norwegian Nobel Committee commented on the transfer of the Peace Prize medal to U.S. President...

Study: The state of the gut microbiome may play a role in the development of social phobia
Researchers decided to delve into this topic to understand the biological mechanisms associated...
Oncological patients remain at high risk group for COVID-19, doctors say
According to a study published in the journal "Healthcare of Kyrgyzstan," patients...
No traces of the explosion. Interim results of the investigation into the plane crash in Aktau published.
The Ministry of Transport of Kazakhstan, through the Department for the Investigation of Transport...
Government Services in Kyrgyzstan Aim to Simplify and Partially Outsource
. As reported by Choro Seyitov, Deputy Minister of Economy and Commerce, the initiative is aimed at...
Why Many Mental Disorders May Be More Similar Than Previously Thought
During the study, the DNA of more than six million people was analyzed, among whom over a million...
In Kyrgyzstan, 117 slaughter points operate with veterinary control
- In Kyrgyzstan, there are 117 slaughter points where strict veterinary control is implemented....

Ministry of Labor: In the third quarter of 2025, more than 800 children found families
In the third quarter of 2025, according to the Ministry of Labor, Social Security, and Migration...

Season of ARVI and influenza. Doctors remind how to protect yourself from infection
Doctors from the Bishkek Health Strengthening Center have addressed the citizens of Kyrgyzstan...

The Audit Chamber of Kyrgyzstan Reveals Violations in "Kyrgyzpharm"
During the audit conducted by the Accounts Chamber, violations were found in the areas of...
A man suspected of beating his mother has been detained
In the Chui region, a 31-year-old man has been detained on suspicion of beating his mother....
ORT-2025. Only 1.7 percent of applicants know the state language at a level below average
During the nationwide testing last year, 57,305 applicants took the test in the state language....

Superflu is rapidly spreading in 34 countries and leading to a sharp increase in hospitalizations
In recent weeks, medical institutions in the UK, Canada, and several other countries have...