Economic Situation
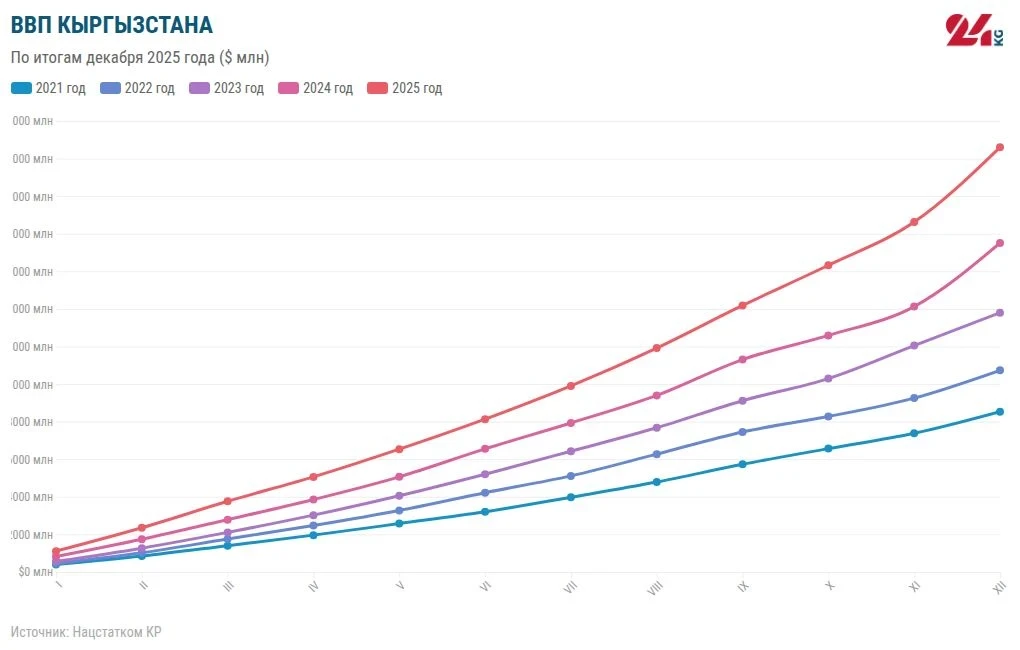
According to the National Bank, the country's economy is demonstrating high growth rates: forecasts suggest that real GDP will grow by 11.1% by the end of 2025. The main sectors contributing to this growth are construction and services. Investments in fixed capital remain at a high level due to increased government funding. Consumer demand is supported by the growth of real incomes, an influx of remittances, and active consumer lending.Inflation Processes
As of January 16 of this year, inflation in Kyrgyzstan stood at 9.4%. There is a slowdown in the growth of prices for food products; however, in the non-food sector and services, prices remain high due to external factors. Annual changes in tariff policy and rising domestic demand also contribute to inflation.The National Bank emphasizes that the main priority of its monetary policy is to reduce inflation to the target level of 5-7% in the medium term, which justifies the maintenance of tight monetary conditions.
In the context of a high level of liquidity in the banking sector, the NB KR actively conducts sterilization operations, which allows for controlling the volume of money supply in the economy. In such conditions, the interbank benchmark interest rate BIR is formed at the lower boundary of the National Bank's interest rate corridor. The domestic currency market remains stable.Inflation continues to be influenced by external factors, including high volatility in global food and commodity markets. The unstable geopolitical situation also contributes to the inflationary background in Kyrgyzstan's partner countries, which, in turn, affects imports. Domestic inflation processes are largely determined by non-monetary factors, such as planned changes in regulated tariffs and rising domestic demand.
These circumstances confirm the necessity of maintaining the current monetary conditions until sustainable prerequisites for slowing inflation are established. Therefore, the National Bank's policy rate remains at 11%.The National Bank does not rule out the possibility of changes in its monetary policy in the event of risks to price stability.