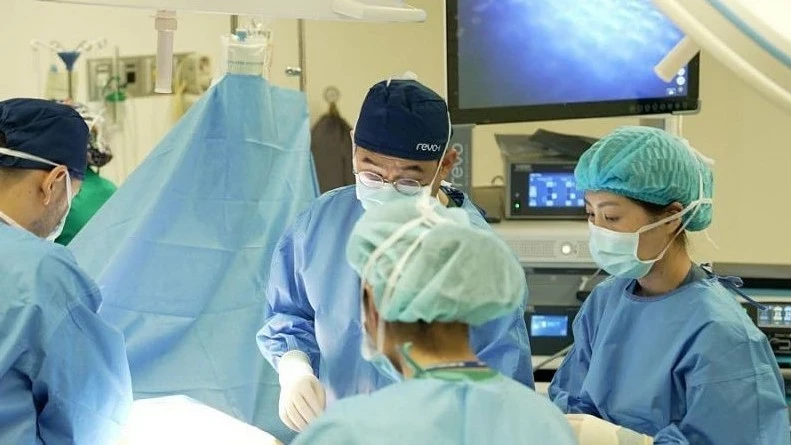
A stem cell transplant has been successfully performed for the first time in Mongolia on a teenager suffering from cancer. This procedure, known as autologous transplantation, was conducted using stem cells from the patient's own body. This was reported by MiddleAsianNews.
The patient was a 15-year-old girl from Mongolia battling leukemia.
The launch of the first successful autologous stem cell transplantation procedure for children took place on December 9, 2025, and was organized by the National Center for Maternal and Child Health in collaboration with the First Central Hospital of Mongolia.
This significant achievement was made possible through cooperation with "Medical Park Hospital" in Turkey and the international organization TIKA, highlighting the importance of training medical personnel through internships and education both domestically and abroad.
The team conducting the transplant included specialists from the Blood Stem Cell Transplantation Center of the First State Central Hospital, as well as doctors and nurses from the National Center for Maternal and Child Health, who have experience in oncology and blood disorders.
The autologous stem cell transplantation procedure carried out in the country met international standards and safety requirements, allowing operations that were previously performed only abroad and significantly improving the quality of cancer treatment for children.
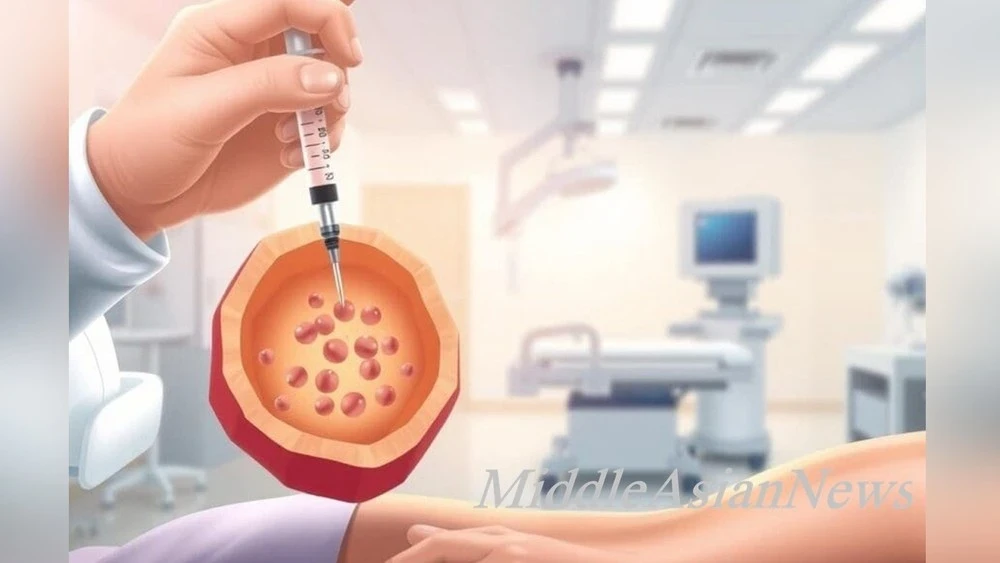
Autologous stem cell transplantation is a method in which a patient's own healthy stem cells (usually collected before high-dose chemotherapy) are extracted, stored, and returned to the body after treatment, helping to restore damaged bone marrow and effectively combat cancer and autoimmune disorders.
This procedure, also known as autogenic or autologous stem cell transplantation, involves the collection and subsequent return of stem cells (undifferentiated cells that can develop into various types of cells) to the patient.
Most commonly, autologous transplantation is performed with hematopoietic stem cells, but it is also successfully used to restore heart cells after heart attacks.
It is important to note that autologous transplantation differs from allogeneic transplantation, where stem cells are taken from another person.